Wine is an open source program for running Windows software on non-Windows operating systems. While it’s most often used on Linux, Wine can run Windows software directly on a Mac, too–without requiring a Windows license or needing Windows running in the background. Installing Wine on Apple Mac. This tutorial explains how to install Wine application on Apple Mac. This application allows to run Embird (native Windows application) on Apple Mac computer. The XQuartz appplication must be installed before installing Wine. Note: Please note, that applications XQuartz and Wine for Apple Mac are not.
- Install With Wine Machine
- Install With Wine Mac Free
- Wine Windows For Mac
- Wine Mac Os X
- Wine On Mac
- Xquartz
- Wine App Mac
- Wine Mac Download
Translations of this page:Français (Translators, please see Discussion page.)
Installing WineHQ packages
Official WineHQ packages of the development and stable branches are available for macOS 10.8 to 10.14 (Wine won't work on macOS Catalina 10.15). Please test these packages and report any bugs at http://bugs.winehq.org.
Prerequisites:
- XQuartz >= 2.7.7
- Gatekeeper must not be set to block unsigned packages.
Installing:
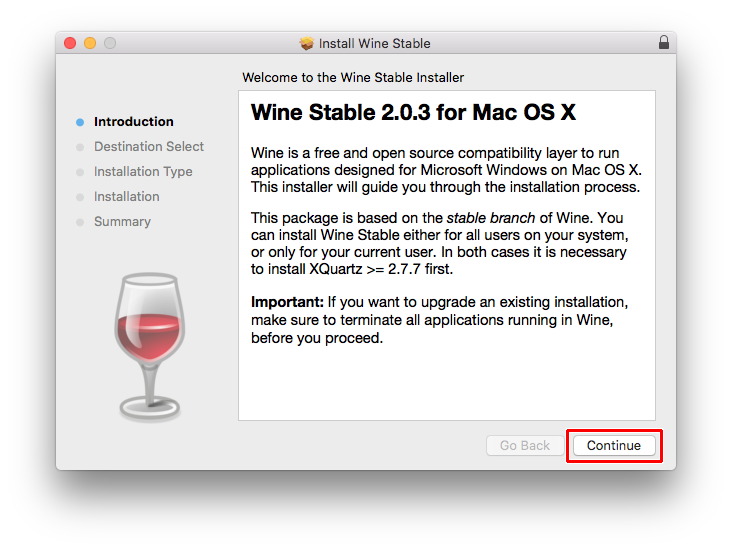
Both .pkg files and tarball archives are available at https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/macosx/download.html.
Installing from a .pkg file is recommended for inexperienced users.
To install from a .pkg file, double-click on the package, and the usual macOS installer wizard should open. The process should be self-explanatory. It is possible to install the package either for all users (needs administrator privileges), or just for your current user. After the installation is finished, you should find an entry 'Wine Staging' or 'Wine Devel' in your Launchpad. By clicking on it, a new Terminal window opens with a short introduction into some important wine commands. You can now directly start wine/winecfg/... from the Terminal, as the PATH variable is set correctly. For user convenience, the package also associates itself with all *.exe files, which means you can run windows executables just by double-clicking on them.
To install from a tarball archive, simply unpack it into any directory. There is no need to set DYLD_* environment variables; all paths are relative, so it should work as long as the directory structure is preserved (you can skip the /usr prefix though using --strip-components 1).
For more information, see https://www.winehq.org/pipermail/wine-devel/2015-December/110990.html and https://www.winehq.org/pipermail/wine-devel/2016-January/111010.html.
Installing Winehq packages using homebrew
Winehq packages can be installed using homebrew
XQuartz can be installed using;
To install wine the following command can be used;
wine-stable, wine-devel or wine-staging packages can be installed using the above example.The advantage of installing via homebrew means wine is available from a standard terminal session
Building Wine
See Building Wine on macOS
Uninstalling Wine
- Remove the source tree and binaries.
Using Homebrew:
Using MacPorts, uninstall the wine package you previously installed:
Replace wine with wine-devel if you installed the development version.
Using Fink:
Replace wine with wine-dev if you installed the development version.
Otherwise and if you used `sudo make install`, revert it:
Then simply delete your local Wine source code directory:
- Clean-up pseudo C: drive and registry entries as well as all programs installed to C:
- Check the hidden directory `$HOME/.local/` where Wine stores some desktop menu entries and icon files as it interoperates with the X.Org Foundation and the Free Desktop.
Note: Files in this directory are unused on macOS unless you use a UNIX window manager and other X11 applications instead of the native MacOS apps.
Third Party Versions
Third party versions of Wine, such as Wineskin, Winebottler, and PlayOnMac, are not supported by WineHQ. If you are using one of those products, please retest in plain Wine before filing bugs, submitting AppDB test reports, or asking for help on the forum or in IRC.
See Also
This tutorial is for intermediate users who want to install and useWine on their computer running macOS.You should already know the basics of how to use the command line.If you don't, read this tutorial first.
What is Wine?
Wine is awesome.No, I'm not talking about the kind you drink,I mean the kind that lets you run Windows apps without theWindows operating system.It's kind of Zen, when you think about it.Oh, and did I mention it's completely free, legal, and open source?
Nowadays, Windows and Mac play nicely together.You can install Windows and Mac side by side and switch between them usingBoot Camp, but that requiresa reboot every time, and you can only use one operating system at a time.You can also use a tool likeParallels Desktop orVMware Fusionto virtualize Windows and run it together with Mac,but virtualization is slow and it takes up a lot of memory.(Your physical computer creates an imaginary 'virtual' computer within itself,and runs Windows on that. That takes a lot of resources!)On top of that, all of these solutions require you to own a legal copyof Windows, which isn't cheap!
Wine is different. When any program runs, it requests resourceslike memory and disk space from the operating system.All that Wine does is make sure that those requests get answered so thatthe program can run correctly. As far as the program knows, everythingis going smoothly because it has everything it needs.It never even realizes that it's not running on Windows!It's simpler than emulating a whole new computer, so it's faster.Since it's just translating requests, you don't need a copy ofthe actual Windows operating system. Plus, Wine is open source,which means people are continually improving it and adding new features.And you can't beat the price!
Will My Program Work With Wine?
A lot of people discover Wine because they have one specific Windows programthat they need to use, and it's the last thing preventing them from switchingto a different operating system. So, the big question is, will it work?The short answer is: probably, but it's worth checking.
The Wine project maintains a database called theAppDB that hasuser reviews of how well specific Windows programs work under Wine.Search for your program and find out! (If it's not listed, that doesn'tnecessarily mean that it won't work — only that you're apparently tryingto use a very obscure program!)
Requirements
To install Wine on your Mac, you will need the following:
- macOS 10.10 (Yosemite) or above (but 10.15 Catalina is not recommended)
- Access to an Admin account, with password
- An internet connection
To check what version of macOS you're running,click on the Apple logo on the far left side of the toolbar,select 'About This Mac', and look at your versionnumber under the big 'macOS' or 'OS X'. If it's 10.10 or higher, you're all set.
Note that Wine does not work well with macOS 10.15 Catalina. Apple removed 32-bit supportin Catalina, which is a critical part of the macOS system that almost all of Wine relies on.You can run 64-bit applications through Wine on Catalina, but very few applications for Windowsare 64-bit. If you need to use Wine, you should not upgrade to Catalina.
You need an Admin account on your Mac because only Admins can install software.You will need to be logged in to this Admin account during the installation.If there is only one account on your computer, it is an Admin account.The account must have a password: if the account has no password,the sudo utility will fail. To set or change your password,go to the Accounts section in System Preferences.
Part 1: Install Homebrew
Homebrew is a package manager that makes installingopen source programs much easier. In particular, trying to installa large program like Wine without the help of a package manager would betremendously difficult.Fortunately, Homebrew itself is simple to install: just open up theTerminal and run this command:
The Terminal will tell you what it's about to do, and ask youif you want to proceed: press Enter to do so.The Terminal may then ask for a password: this is the passwordto the Admin account on your computer. As a security measure,the Terminal does not display anything as you type, not evenasterisks (*). Type your password anyway, and press Enter. If you get somekind of error, it might be because the Admin account doesn't have apassword set. Setting a password is required.
Installing Homebrew should only take a few seconds or minutes(depending on the speed of your internet connection). When it's done,the Terminal will say that the installation was successful, and ask you torun brew doctor. Do as it suggests:
This will make Homebrew inspect your system and make sure that everythingis set up correctly. If the Terminal informs you of any issues, you'll needto fix them yourself, and then run brew doctor again to verify that youfixed them correctly. When everything is set up correctly, you'll see themessage Your system is ready to brew, and you can move on to the next partof the tutorial.
Note: If Homebrew tells you that you need to agree to the Xcode license,you can do that by running:
The Terminal window will fill up with the Xcode license:read it, type agree and hit enter to agree to the license.
Part 2: Install Wine Using Homebrew
Now we get to actually install Wine! We'll let Homebrew do all the work,all you have to do is tell it what you want with this command:
Let's break down this command into parts. brew refers to Homebrew, whichyou just installed. cask refers toHomebrew Cask,an extension to Homebrew that is used to install GUI application on yourcomputer. (GUI stands for 'Graphical User Interface'. A GUI application isan app that you can see running, as opposed to invisibly runningin the background.) install refers to the fact that you're askingHomebrew Cask to install something on your computer, and wine-stableis the name of the thing that you want it to install. Wine has a 'stable' versionand a 'devel' version: you probably want stable, since it should have fewer bugs.
When you run this command, Homebrew will start automatically downloadingand installing software onto your computer. It might start by installingsoftware that has a totally different name: that's fine! Like most complexapplications, Wine doesn't work alone -- it relies on several other pieces of software torun correctly. These are called 'dependencies', and Homebrew is smart enoughto install them for you automatically when necessary.
While it's working, Homebrew will display messages and progress bars on the Terminal to let you know what it's doing. When it's done installing Wine, it will stop displaying messages and wait for you to type in a new command. When that happens, move on to the next step!
Part 3: Install Windows Programs Using Wine
To install a Windows program, first download the installer file:it should end with .exe. Remember the location you put it, and open upthe Terminal again. cd to the location, and use ls to make sure you cansee the installer file. (Note: if you do not know what cd and ls are,you should learn how to use the command linebefore using Wine.)
Once you are in the correct directory, run the installer through Wineby running the following command in the Terminal:
Where $INSTALLER is the name of the installer file. For example,if the installer file is named setup.exe, you would run:
A window will pop up with a regular graphical Windows installer.Click through it, and you're done!
Part 4: Run Windows Programs Using Wine
Open up the Terminal and run this to get to your Program Files folder:
Run ls to see what programs you have installed. Pick a program,and enter its directory using cd. (If the folder has a space in it,you must type a before the space. For example, Program Files.If you're having problems, try using tab autocomplete.)There should be a file that ends in .exe: this is the program file.Type this into Terminal:
Where $PROGRAM is the name of the .exe file. For example, if the programfile is named STARCRAFT.EXE, you would run:
The program will pop up in a new window, ready to use!Enjoy using Windows on your Mac, freely and legally!
Making a Dock Icon
Many people want to be able to run Windows programs the same waythey run other programs on the Mac: by clicking an icon in the Dock.Wine isn't specifically designed to support this, but with a little trickery,we can make it do what we want.
Note: Wine prints out error messages in the Terminal when something goes wrong.By launching Windows programs via a Dock icon, you are sidestepping theTerminal, which means that if something does go wrong and Wine has to quit,it will not be able to tell you what the problem was. The first stepto solving a problem is knowing what it is, so without running Winefrom the Terminal, you won't be able to fix it, and neither will anyone else.Running from the Dock is fine as long as your program seems to be workingcorrectly, but if it crashes, the first thing you should try is running itfrom the Terminal instead: it won't prevent the program from crashing,but it will give you some clues on how to fix the problem.
Install With Wine Machine
In order to launch a Windows program via the Dock, we're going towrite an AppleScriptthat launches the program for us, and then putthat AppleScript in the Dock. Essentially, we're writing a program ourselves!Don't worry, it's easy enough. There is a program on your computerthat is designed for helping you write AppleScripts:it's called 'Script Editor', and you can find it in the/Applications/Utilities directory of your computer,same as the Terminal itself.
Install With Wine Mac Free
Open up the Script Editor. You should see a window with a large areayou can type in near the top: this is where you write your AppleScript.In that area, type the following text:
You'll need to replace $PATH_TO_PROGRAM with the path from theProgram Files directory to your program executable. You can see thatyou're simply telling the AppleScript to run a line of code in the Terminal:the same line of code that you could run to start your Windows program.
Wine Windows For Mac
Next, press the Compile button at the top of the window.The text should become colored to indicate that Script Editorunderstands what you wrote. You can also try pressing the Run buttonto run your script: it should open the Windows program successfully.
Lastly, save your script. You can give it whatever name you'd like,but be sure to select File Format: Application in the save options,and leave Startup Screen unchecked.
Wine Mac Os X
Open up the Finder, go to where you saved your script, and drag thatfile to your Dock. It should stay there, just like a real application — because it is a real application! However, all it does is runthat launcher command for you, so you can move the application around,rename it, or even delete it, and it won't affect the Windows programthat you're running.
Wine On Mac
Keeping Wine Up to Date
Xquartz
Wine is an open source program. That means that programmersaround the world are continually improving it, adding new featuresand squashing bugs. If you don't update Wine, though, it will neverget those improvements, so it's generally a good idea to check for updatesevery so often. We can use Homebrew to keep Wine up to date: it's easy!Just run this command:
With this command, Homebrew will first update itself, if any updatesare available. It will then find all the outdated software it knows about(including Wine) and upgrade them all to the latest version.Checking for updates isn't strictly necessary, as Wine runs quite wellcurrently. However, it's a good idea to run this command every few monthsor so.
Wine App Mac
Uninstalling Wine and Homebrew
Wine Mac Download
If you try Wine and you don't like it, uninstalling it is easy.Just run this command:
And Homebrew will helpfully remove Wine from your computer.However, in order to install Wine, Homebrew also had to install many othersmall programs that Wine relies upon to work correctly.(That's why the install process takes so long!)If you want to remove these as well,run this script:
That script will remove everthing that you installed in this tutorial,including Homebrew, Wine, and all the other programs Homebrew installedto get Wine to work correctly.
Please enable JavaScript to view the comments powered by Disqus.